Chapter 14 – Deep Computer Vision Using Convolutional Neural Networks
This notebook contains all the sample code in chapter 14.
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
Setup
First, let’s import a few common modules, ensure MatplotLib plots figures inline and prepare a function to save the figures. We also check that Python 3.5 or later is installed (although Python 2.x may work, it is deprecated so we strongly recommend you use Python 3 instead), as well as Scikit-Learn ≥0.20 and TensorFlow ≥2.0.
# Python ≥3.5 is required
import sys
assert sys.version_info >= (3, 5)
# Scikit-Learn ≥0.20 is required
import sklearn
assert sklearn.__version__ >= "0.20"
try:
# %tensorflow_version only exists in Colab.
%tensorflow_version 2.x
IS_COLAB = True
except Exception:
IS_COLAB = False
# TensorFlow ≥2.0 is required
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
assert tf.__version__ >= "2.0"
if not tf.test.is_gpu_available():
print("No GPU was detected. CNNs can be very slow without a GPU.")
if IS_COLAB:
print("Go to Runtime > Change runtime and select a GPU hardware accelerator.")
# Common imports
import numpy as np
import os
# to make this notebook's output stable across runs
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# To plot pretty figures
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)
mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)
mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)
# Where to save the figures
PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "."
CHAPTER_ID = "cnn"
IMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "images", CHAPTER_ID)
os.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)
def save_fig(fig_id, tight_layout=True, fig_extension="png", resolution=300):
path = os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id + "." + fig_extension)
print("Saving figure", fig_id)
if tight_layout:
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(path, format=fig_extension, dpi=resolution)
A couple utility functions to plot grayscale and RGB images:
def plot_image(image):
plt.imshow(image, cmap="gray", interpolation="nearest")
plt.axis("off")
def plot_color_image(image):
plt.imshow(image, interpolation="nearest")
plt.axis("off")
What is a Convolution?
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_sample_image
# Load sample images
china = load_sample_image("china.jpg") / 255
flower = load_sample_image("flower.jpg") / 255
images = np.array([china, flower])
batch_size, height, width, channels = images.shape
# Create 2 filters
filters = np.zeros(shape=(7, 7, channels, 2), dtype=np.float32)
filters[:, 3, :, 0] = 1 # vertical line
filters[3, :, :, 1] = 1 # horizontal line
outputs = tf.nn.conv2d(images, filters, strides=1, padding="SAME")
plt.imshow(outputs[0, :, :, 1], cmap="gray") # plot 1st image's 2nd feature map
plt.axis("off") # Not shown in the book
plt.show()
for image_index in (0, 1):
for feature_map_index in (0, 1):
plt.subplot(2, 2, image_index * 2 + feature_map_index + 1)
plot_image(outputs[image_index, :, :, feature_map_index])
plt.show()
def crop(images):
return images[150:220, 130:250]
plot_image(crop(images[0, :, :, 0]))
save_fig("china_original", tight_layout=False)
plt.show()
for feature_map_index, filename in enumerate(["china_vertical", "china_horizontal"]):
plot_image(crop(outputs[0, :, :, feature_map_index]))
save_fig(filename, tight_layout=False)
plt.show()
plot_image(filters[:, :, 0, 0])
plt.show()
plot_image(filters[:, :, 0, 1])
plt.show()
Convolutional Layer
Using keras.layers.Conv2D():
conv = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, strides=1,
padding="SAME", activation="relu")
plot_image(crop(outputs[0, :, :, 0]))
plt.show()
VALID vs SAME padding
def feature_map_size(input_size, kernel_size, strides=1, padding="SAME"):
if padding == "SAME":
return (input_size - 1) // strides + 1
else:
return (input_size - kernel_size) // strides + 1
def pad_before_and_padded_size(input_size, kernel_size, strides=1):
fmap_size = feature_map_size(input_size, kernel_size, strides)
padded_size = max((fmap_size - 1) * strides + kernel_size, input_size)
pad_before = (padded_size - input_size) // 2
return pad_before, padded_size
def manual_same_padding(images, kernel_size, strides=1):
if kernel_size == 1:
return images.astype(np.float32)
batch_size, height, width, channels = images.shape
top_pad, padded_height = pad_before_and_padded_size(height, kernel_size, strides)
left_pad, padded_width = pad_before_and_padded_size(width, kernel_size, strides)
padded_shape = [batch_size, padded_height, padded_width, channels]
padded_images = np.zeros(padded_shape, dtype=np.float32)
padded_images[:, top_pad:height+top_pad, left_pad:width+left_pad, :] = images
return padded_images
Using "SAME" padding is equivalent to padding manually using manual_same_padding() then using "VALID" padding (confusingly, "VALID" padding means no padding at all):
kernel_size = 7
strides = 2
conv_valid = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=1, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=strides, padding="VALID")
conv_same = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=1, kernel_size=kernel_size, strides=strides, padding="SAME")
valid_output = conv_valid(manual_same_padding(images, kernel_size, strides))
# Need to call build() so conv_same's weights get created
conv_same.build(tf.TensorShape(images.shape))
# Copy the weights from conv_valid to conv_same
conv_same.set_weights(conv_valid.get_weights())
same_output = conv_same(images.astype(np.float32))
assert np.allclose(valid_output.numpy(), same_output.numpy())
Pooling layer
Max pooling
max_pool = keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2)
cropped_images = np.array([crop(image) for image in images])
output = max_pool(cropped_images)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
gs = mpl.gridspec.GridSpec(nrows=1, ncols=2, width_ratios=[2, 1])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
ax1.set_title("Input", fontsize=14)
ax1.imshow(cropped_images[0]) # plot the 1st image
ax1.axis("off")
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
ax2.set_title("Output", fontsize=14)
ax2.imshow(output[0]) # plot the output for the 1st image
ax2.axis("off")
save_fig("china_max_pooling")
plt.show()
Depth-wise pooling
class DepthMaxPool(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, pool_size, strides=None, padding="VALID", **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
if strides is None:
strides = pool_size
self.pool_size = pool_size
self.strides = strides
self.padding = padding
def call(self, inputs):
return tf.nn.max_pool(inputs,
ksize=(1, 1, 1, self.pool_size),
strides=(1, 1, 1, self.pool_size),
padding=self.padding)
depth_pool = DepthMaxPool(3)
with tf.device("/cpu:0"): # there is no GPU-kernel yet
depth_output = depth_pool(cropped_images)
depth_output.shape
Or just use a Lambda layer:
depth_pool = keras.layers.Lambda(lambda X: tf.nn.max_pool(
X, ksize=(1, 1, 1, 3), strides=(1, 1, 1, 3), padding="VALID"))
with tf.device("/cpu:0"): # there is no GPU-kernel yet
depth_output = depth_pool(cropped_images)
depth_output.shape
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title("Input", fontsize=14)
plot_color_image(cropped_images[0]) # plot the 1st image
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.title("Output", fontsize=14)
plot_image(depth_output[0, ..., 0]) # plot the output for the 1st image
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
Average pooling
avg_pool = keras.layers.AvgPool2D(pool_size=2)
output_avg = avg_pool(cropped_images)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
gs = mpl.gridspec.GridSpec(nrows=1, ncols=2, width_ratios=[2, 1])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
ax1.set_title("Input", fontsize=14)
ax1.imshow(cropped_images[0]) # plot the 1st image
ax1.axis("off")
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
ax2.set_title("Output", fontsize=14)
ax2.imshow(output_avg[0]) # plot the output for the 1st image
ax2.axis("off")
plt.show()
Global Average Pooling
global_avg_pool = keras.layers.GlobalAvgPool2D()
global_avg_pool(cropped_images)
output_global_avg2 = keras.layers.Lambda(lambda X: tf.reduce_mean(X, axis=[1, 2]))
output_global_avg2(cropped_images)
Tackling Fashion MNIST With a CNN
(X_train_full, y_train_full), (X_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
X_train, X_valid = X_train_full[:-5000], X_train_full[-5000:]
y_train, y_valid = y_train_full[:-5000], y_train_full[-5000:]
X_mean = X_train.mean(axis=0, keepdims=True)
X_std = X_train.std(axis=0, keepdims=True) + 1e-7
X_train = (X_train - X_mean) / X_std
X_valid = (X_valid - X_mean) / X_std
X_test = (X_test - X_mean) / X_std
X_train = X_train[..., np.newaxis]
X_valid = X_valid[..., np.newaxis]
X_test = X_test[..., np.newaxis]
from functools import partial
DefaultConv2D = partial(keras.layers.Conv2D,
kernel_size=3, activation='relu', padding="SAME")
model = keras.models.Sequential([
DefaultConv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=7, input_shape=[28, 28, 1]),
keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2),
DefaultConv2D(filters=128),
DefaultConv2D(filters=128),
keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2),
DefaultConv2D(filters=256),
DefaultConv2D(filters=256),
keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(units=64, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(units=10, activation='softmax'),
])
model.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer="nadam", metrics=["accuracy"])
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=10, validation_data=[X_valid, y_valid])
score = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
X_new = X_test[:10] # pretend we have new images
y_pred = model.predict(X_new)
ResNet-34
DefaultConv2D = partial(keras.layers.Conv2D, kernel_size=3, strides=1,
padding="SAME", use_bias=False)
class ResidualUnit(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, filters, strides=1, activation="relu", **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.activation = keras.activations.get(activation)
self.main_layers = [
DefaultConv2D(filters, strides=strides),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
self.activation,
DefaultConv2D(filters),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization()]
self.skip_layers = []
if strides > 1:
self.skip_layers = [
DefaultConv2D(filters, kernel_size=1, strides=strides),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization()]
def call(self, inputs):
Z = inputs
for layer in self.main_layers:
Z = layer(Z)
skip_Z = inputs
for layer in self.skip_layers:
skip_Z = layer(skip_Z)
return self.activation(Z + skip_Z)
model = keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(DefaultConv2D(64, kernel_size=7, strides=2,
input_shape=[224, 224, 3]))
model.add(keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
model.add(keras.layers.Activation("relu"))
model.add(keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding="SAME"))
prev_filters = 64
for filters in [64] * 3 + [128] * 4 + [256] * 6 + [512] * 3:
strides = 1 if filters == prev_filters else 2
model.add(ResidualUnit(filters, strides=strides))
prev_filters = filters
model.add(keras.layers.GlobalAvgPool2D())
model.add(keras.layers.Flatten())
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax"))
model.summary()
Using a Pretrained Model
model = keras.applications.resnet50.ResNet50(weights="imagenet")
images_resized = tf.image.resize(images, [224, 224])
plot_color_image(images_resized[0])
plt.show()
images_resized = tf.image.resize_with_pad(images, 224, 224, antialias=True)
plot_color_image(images_resized[0])
images_resized = tf.image.resize_with_crop_or_pad(images, 224, 224)
plot_color_image(images_resized[0])
plt.show()
china_box = [0, 0.03, 1, 0.68]
flower_box = [0.19, 0.26, 0.86, 0.7]
images_resized = tf.image.crop_and_resize(images, [china_box, flower_box], [0, 1], [224, 224])
plot_color_image(images_resized[0])
plt.show()
plot_color_image(images_resized[1])
plt.show()
inputs = keras.applications.resnet50.preprocess_input(images_resized * 255)
Y_proba = model.predict(inputs)
Y_proba.shape
top_K = keras.applications.resnet50.decode_predictions(Y_proba, top=3)
for image_index in range(len(images)):
print("Image #{}".format(image_index))
for class_id, name, y_proba in top_K[image_index]:
print(" {} - {:12s} {:.2f}%".format(class_id, name, y_proba * 100))
print()
Pretrained Models for Transfer Learning
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
dataset, info = tfds.load("tf_flowers", as_supervised=True, with_info=True)
info.splits
info.splits["train"]
class_names = info.features["label"].names
class_names
n_classes = info.features["label"].num_classes
dataset_size = info.splits["train"].num_examples
dataset_size
test_split, valid_split, train_split = tfds.Split.TRAIN.subsplit([10, 15, 75])
test_set_raw = tfds.load("tf_flowers", split=test_split, as_supervised=True)
valid_set_raw = tfds.load("tf_flowers", split=valid_split, as_supervised=True)
train_set_raw = tfds.load("tf_flowers", split=train_split, as_supervised=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
index = 0
for image, label in train_set_raw.take(9):
index += 1
plt.subplot(3, 3, index)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title("Class: {}".format(class_names[label]))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
Basic preprocessing:
def preprocess(image, label):
resized_image = tf.image.resize(image, [224, 224])
final_image = keras.applications.xception.preprocess_input(resized_image)
return final_image, label
Slightly fancier preprocessing (but you could add much more data augmentation):
def central_crop(image):
shape = tf.shape(image)
min_dim = tf.reduce_min([shape[0], shape[1]])
top_crop = (shape[0] - min_dim) // 4
bottom_crop = shape[0] - top_crop
left_crop = (shape[1] - min_dim) // 4
right_crop = shape[1] - left_crop
return image[top_crop:bottom_crop, left_crop:right_crop]
def random_crop(image):
shape = tf.shape(image)
min_dim = tf.reduce_min([shape[0], shape[1]]) * 90 // 100
return tf.image.random_crop(image, [min_dim, min_dim, 3])
def preprocess(image, label, randomize=False):
if randomize:
cropped_image = random_crop(image)
cropped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(cropped_image)
else:
cropped_image = central_crop(image)
resized_image = tf.image.resize(cropped_image, [224, 224])
final_image = keras.applications.xception.preprocess_input(resized_image)
return final_image, label
batch_size = 32
train_set = train_set_raw.shuffle(1000).repeat()
train_set = train_set.map(partial(preprocess, randomize=True)).batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
valid_set = valid_set_raw.map(preprocess).batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
test_set = test_set_raw.map(preprocess).batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for X_batch, y_batch in train_set.take(1):
for index in range(9):
plt.subplot(3, 3, index + 1)
plt.imshow(X_batch[index] / 2 + 0.5)
plt.title("Class: {}".format(class_names[y_batch[index]]))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for X_batch, y_batch in test_set.take(1):
for index in range(9):
plt.subplot(3, 3, index + 1)
plt.imshow(X_batch[index] / 2 + 0.5)
plt.title("Class: {}".format(class_names[y_batch[index]]))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
base_model = keras.applications.xception.Xception(weights="imagenet",
include_top=False)
avg = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(base_model.output)
output = keras.layers.Dense(n_classes, activation="softmax")(avg)
model = keras.models.Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=output)
for index, layer in enumerate(base_model.layers):
print(index, layer.name)
for layer in base_model.layers:
layer.trainable = False
optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.2, momentum=0.9, decay=0.01)
model.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=["accuracy"])
history = model.fit(train_set,
steps_per_epoch=int(0.75 * dataset_size / batch_size),
validation_data=valid_set,
validation_steps=int(0.15 * dataset_size / batch_size),
epochs=5)
for layer in base_model.layers:
layer.trainable = True
optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.9,
nesterov=True, decay=0.001)
model.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=["accuracy"])
history = model.fit(train_set,
steps_per_epoch=int(0.75 * dataset_size / batch_size),
validation_data=valid_set,
validation_steps=int(0.15 * dataset_size / batch_size),
epochs=40)
Classification and Localization
base_model = keras.applications.xception.Xception(weights="imagenet",
include_top=False)
avg = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(base_model.output)
class_output = keras.layers.Dense(n_classes, activation="softmax")(avg)
loc_output = keras.layers.Dense(4)(avg)
model = keras.models.Model(inputs=base_model.input,
outputs=[class_output, loc_output])
model.compile(loss=["sparse_categorical_crossentropy", "mse"],
loss_weights=[0.8, 0.2], # depends on what you care most about
optimizer=optimizer, metrics=["accuracy"])
def add_random_bounding_boxes(images, labels):
fake_bboxes = tf.random.uniform([tf.shape(images)[0], 4])
return images, (labels, fake_bboxes)
fake_train_set = train_set.take(5).repeat(2).map(add_random_bounding_boxes)
model.fit(fake_train_set, steps_per_epoch=5, epochs=2)
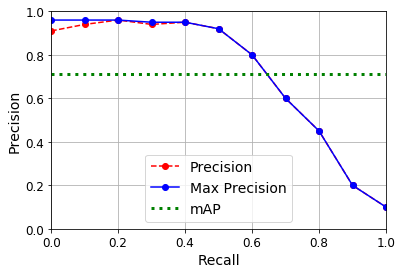
Mean Average Precision (mAP)
def maximum_precisions(precisions):
return np.flip(np.maximum.accumulate(np.flip(precisions)))
recalls = np.linspace(0, 1, 11)
precisions = [0.91, 0.94, 0.96, 0.94, 0.95, 0.92, 0.80, 0.60, 0.45, 0.20, 0.10]
max_precisions = maximum_precisions(precisions)
mAP = max_precisions.mean()
plt.plot(recalls, precisions, "ro--", label="Precision")
plt.plot(recalls, max_precisions, "bo-", label="Max Precision")
plt.xlabel("Recall")
plt.ylabel("Precision")
plt.plot([0, 1], [mAP, mAP], "g:", linewidth=3, label="mAP")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 1])
plt.legend(loc="lower center", fontsize=14)
plt.show()
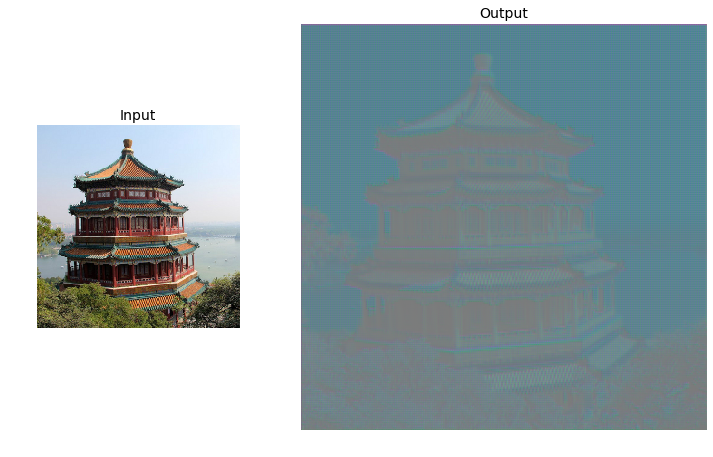
Transpose convolutions:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
X = images_resized.numpy()
conv_transpose = keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters=5, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="VALID")
output = conv_transpose(X)
output.shape
def normalize(X):
return (X - tf.reduce_min(X)) / (tf.reduce_max(X) - tf.reduce_min(X))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
gs = mpl.gridspec.GridSpec(nrows=1, ncols=2, width_ratios=[1, 2])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
ax1.set_title("Input", fontsize=14)
ax1.imshow(X[0]) # plot the 1st image
ax1.axis("off")
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
ax2.set_title("Output", fontsize=14)
ax2.imshow(normalize(output[0, ..., :3]), interpolation="bicubic") # plot the output for the 1st image
ax2.axis("off")
plt.show()
def upscale_images(images, stride, kernel_size):
batch_size, height, width, channels = images.shape
upscaled = np.zeros((batch_size,
(height - 1) * stride + 2 * kernel_size - 1,
(width - 1) * stride + 2 * kernel_size - 1,
channels))
upscaled[:,
kernel_size - 1:(height - 1) * stride + kernel_size:stride,
kernel_size - 1:(width - 1) * stride + kernel_size:stride,
:] = images
return upscaled
upscaled = upscale_images(X, stride=2, kernel_size=3)
weights, biases = conv_transpose.weights
reversed_filters = np.flip(weights.numpy(), axis=[0, 1])
reversed_filters = np.transpose(reversed_filters, [0, 1, 3, 2])
manual_output = tf.nn.conv2d(upscaled, reversed_filters, strides=1, padding="VALID")
def normalize(X):
return (X - tf.reduce_min(X)) / (tf.reduce_max(X) - tf.reduce_min(X))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
gs = mpl.gridspec.GridSpec(nrows=1, ncols=3, width_ratios=[1, 2, 2])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
ax1.set_title("Input", fontsize=14)
ax1.imshow(X[0]) # plot the 1st image
ax1.axis("off")
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
ax2.set_title("Upscaled", fontsize=14)
ax2.imshow(upscaled[0], interpolation="bicubic")
ax2.axis("off")
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 2])
ax3.set_title("Output", fontsize=14)
ax3.imshow(normalize(manual_output[0, ..., :3]), interpolation="bicubic") # plot the output for the 1st image
ax3.axis("off")
plt.show()
np.allclose(output, manual_output.numpy(), atol=1e-7)
Exercises
1. to 8.
See appendix A.
9. High Accuracy CNN for MNIST
Exercise: Build your own CNN from scratch and try to achieve the highest possible accuracy on MNIST.
10. Use transfer learning for large image classification
10.1)
Create a training set containing at least 100 images per class. For example, you could classify your own pictures based on the location (beach, mountain, city, etc.), or alternatively you can just use an existing dataset (e.g., from TensorFlow Datasets).
10.2)
Split it into a training set, a validation set and a test set.
10.3)
Build the input pipeline, including the appropriate preprocessing operations, and optionally add data augmentation.
10.4)
Fine-tune a pretrained model on this dataset.
11.
Exercise: Go through TensorFlow’s DeepDream tutorial. It is a fun way to familiarize yourself with various ways of visualizing the patterns learned by a CNN, and to generate art using Deep Learning.
Simply download the notebook and follow its instructions. For extra fun, you can produce a series of images, by repeatedly zooming in and running the DeepDream algorithm: using a tool such as ffmpeg you can then create a video from these images. For example, here is a DeepDream video I made… as you will see, it quickly turns into a nightmare. ;-) You can find hundreds of similar videos (often much more artistic) on the web.