Chapter 17 – Autoencoders and GANs
This notebook contains all the sample code in chapter 17.
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
Setup
First, let’s import a few common modules, ensure MatplotLib plots figures inline and prepare a function to save the figures. We also check that Python 3.5 or later is installed (although Python 2.x may work, it is deprecated so we strongly recommend you use Python 3 instead), as well as Scikit-Learn ≥0.20 and TensorFlow ≥2.0.
# Python ≥3.5 is required
import sys
assert sys.version_info >= (3, 5)
# Scikit-Learn ≥0.20 is required
import sklearn
assert sklearn.__version__ >= "0.20"
try:
# %tensorflow_version only exists in Colab.
%tensorflow_version 2.x
IS_COLAB = True
except Exception:
IS_COLAB = False
# TensorFlow ≥2.0 is required
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
assert tf.__version__ >= "2.0"
if not tf.test.is_gpu_available():
print("No GPU was detected. LSTMs and CNNs can be very slow without a GPU.")
if IS_COLAB:
print("Go to Runtime > Change runtime and select a GPU hardware accelerator.")
# Common imports
import numpy as np
import os
# to make this notebook's output stable across runs
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# To plot pretty figures
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)
mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)
mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)
# Where to save the figures
PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "."
CHAPTER_ID = "autoencoders"
IMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "images", CHAPTER_ID)
os.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)
def save_fig(fig_id, tight_layout=True, fig_extension="png", resolution=300):
path = os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id + "." + fig_extension)
print("Saving figure", fig_id)
if tight_layout:
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(path, format=fig_extension, dpi=resolution)
A couple utility functions to plot grayscale 28x28 image:
def plot_image(image):
plt.imshow(image, cmap="binary")
plt.axis("off")
PCA with a linear Autoencoder
Build 3D dataset:
np.random.seed(4)
def generate_3d_data(m, w1=0.1, w2=0.3, noise=0.1):
angles = np.random.rand(m) * 3 * np.pi / 2 - 0.5
data = np.empty((m, 3))
data[:, 0] = np.cos(angles) + np.sin(angles)/2 + noise * np.random.randn(m) / 2
data[:, 1] = np.sin(angles) * 0.7 + noise * np.random.randn(m) / 2
data[:, 2] = data[:, 0] * w1 + data[:, 1] * w2 + noise * np.random.randn(m)
return data
X_train = generate_3d_data(60)
X_train = X_train - X_train.mean(axis=0, keepdims=0)
Now let’s build the Autoencoder…
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
encoder = keras.models.Sequential([keras.layers.Dense(2, input_shape=[3])])
decoder = keras.models.Sequential([keras.layers.Dense(3, input_shape=[2])])
autoencoder = keras.models.Sequential([encoder, decoder])
autoencoder.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.5))
history = autoencoder.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=20)
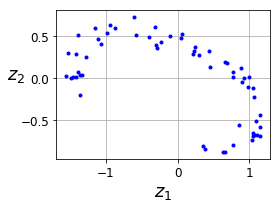
codings = encoder.predict(X_train)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4,3))
plt.plot(codings[:,0], codings[:, 1], "b.")
plt.xlabel("$z_1$", fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel("$z_2$", fontsize=18, rotation=0)
plt.grid(True)
save_fig("linear_autoencoder_pca_plot")
plt.show()
Stacked Autoencoders
Let’s use MNIST:
(X_train_full, y_train_full), (X_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
X_train_full = X_train_full.astype(np.float32) / 255
X_test = X_test.astype(np.float32) / 255
X_train, X_valid = X_train_full[:-5000], X_train_full[-5000:]
y_train, y_valid = y_train_full[:-5000], y_train_full[-5000:]
Train all layers at once
Let’s build a stacked Autoencoder with 3 hidden layers and 1 output layer (i.e., 2 stacked Autoencoders).
def rounded_accuracy(y_true, y_pred):
return keras.metrics.binary_accuracy(tf.round(y_true), tf.round(y_pred))
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
stacked_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="selu"),
])
stacked_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[30]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
stacked_ae = keras.models.Sequential([stacked_encoder, stacked_decoder])
stacked_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.5), metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = stacked_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=20,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
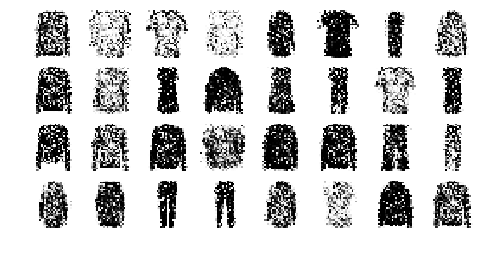
This function processes a few test images through the autoencoder and displays the original images and their reconstructions:
def show_reconstructions(model, images=X_valid, n_images=5):
reconstructions = model.predict(images[:n_images])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(n_images * 1.5, 3))
for image_index in range(n_images):
plt.subplot(2, n_images, 1 + image_index)
plot_image(images[image_index])
plt.subplot(2, n_images, 1 + n_images + image_index)
plot_image(reconstructions[image_index])
show_reconstructions(stacked_ae)
save_fig("reconstruction_plot")
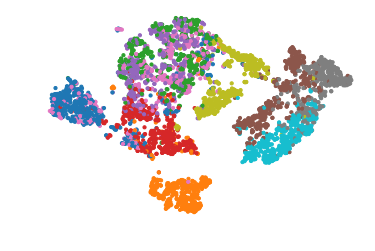
Visualizing Fashion MNIST
np.random.seed(42)
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
X_valid_compressed = stacked_encoder.predict(X_valid)
tsne = TSNE()
X_valid_2D = tsne.fit_transform(X_valid_compressed)
X_valid_2D = (X_valid_2D - X_valid_2D.min()) / (X_valid_2D.max() - X_valid_2D.min())
plt.scatter(X_valid_2D[:, 0], X_valid_2D[:, 1], c=y_valid, s=10, cmap="tab10")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
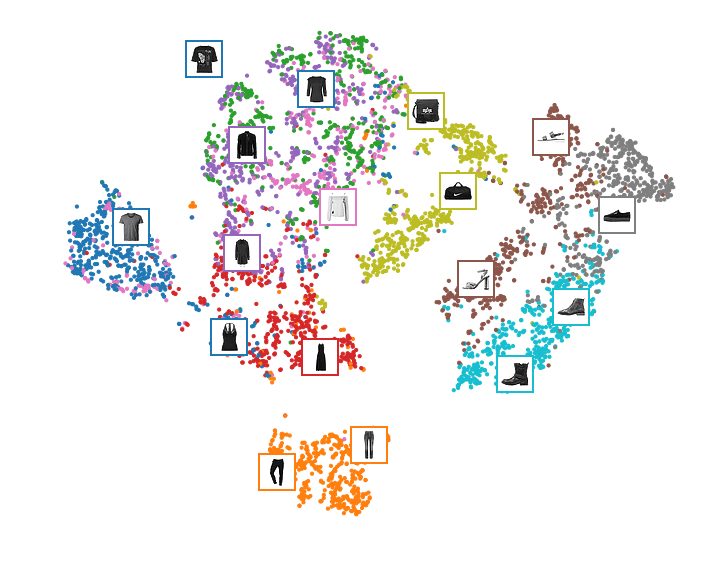
Let’s make this diagram a bit prettier:
# adapted from https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/manifold/plot_lle_digits.html
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
cmap = plt.cm.tab10
plt.scatter(X_valid_2D[:, 0], X_valid_2D[:, 1], c=y_valid, s=10, cmap=cmap)
image_positions = np.array([[1., 1.]])
for index, position in enumerate(X_valid_2D):
dist = np.sum((position - image_positions) ** 2, axis=1)
if np.min(dist) > 0.02: # if far enough from other images
image_positions = np.r_[image_positions, [position]]
imagebox = mpl.offsetbox.AnnotationBbox(
mpl.offsetbox.OffsetImage(X_valid[index], cmap="binary"),
position, bboxprops={"edgecolor": cmap(y_valid[index]), "lw": 2})
plt.gca().add_artist(imagebox)
plt.axis("off")
save_fig("fashion_mnist_visualization_plot")
plt.show()
Tying weights
It is common to tie the weights of the encoder and the decoder, by simply using the transpose of the encoder’s weights as the decoder weights. For this, we need to use a custom layer.
class DenseTranspose(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, dense, activation=None, **kwargs):
self.dense = dense
self.activation = keras.activations.get(activation)
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, batch_input_shape):
self.biases = self.add_weight(name="bias",
shape=[self.dense.input_shape[-1]],
initializer="zeros")
super().build(batch_input_shape)
def call(self, inputs):
z = tf.matmul(inputs, self.dense.weights[0], transpose_b=True)
return self.activation(z + self.biases)
keras.backend.clear_session()
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
dense_1 = keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu")
dense_2 = keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="selu")
tied_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
dense_1,
dense_2
])
tied_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
DenseTranspose(dense_2, activation="selu"),
DenseTranspose(dense_1, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
tied_ae = keras.models.Sequential([tied_encoder, tied_decoder])
tied_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.5), metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = tied_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
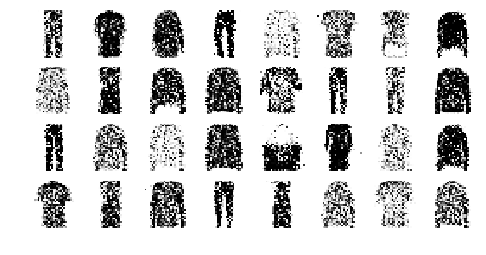
show_reconstructions(tied_ae)
plt.show()
Training one Autoencoder at a time
def train_autoencoder(n_neurons, X_train, X_valid, loss, optimizer,
n_epochs=10, output_activation=None, metrics=None):
n_inputs = X_train.shape[-1]
encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(n_neurons, activation="selu", input_shape=[n_inputs])
])
decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(n_inputs, activation=output_activation),
])
autoencoder = keras.models.Sequential([encoder, decoder])
autoencoder.compile(optimizer, loss, metrics=metrics)
autoencoder.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=n_epochs,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
return encoder, decoder, encoder(X_train), encoder(X_valid)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
K = keras.backend
X_train_flat = K.batch_flatten(X_train) # equivalent to .reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
X_valid_flat = K.batch_flatten(X_valid)
enc1, dec1, X_train_enc1, X_valid_enc1 = train_autoencoder(
100, X_train_flat, X_valid_flat, "binary_crossentropy",
keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.5), output_activation="sigmoid",
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
enc2, dec2, _, _ = train_autoencoder(
30, X_train_enc1, X_valid_enc1, "mse", keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.05),
output_activation="selu")
stacked_ae_1_by_1 = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
enc1, enc2, dec2, dec1,
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
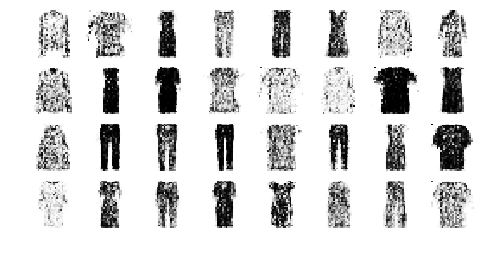
show_reconstructions(stacked_ae_1_by_1)
plt.show()
stacked_ae_1_by_1.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.1), metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = stacked_ae_1_by_1.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(stacked_ae_1_by_1)
plt.show()
Using Convolutional Layers Instead of Dense Layers
Let’s build a stacked Autoencoder with 3 hidden layers and 1 output layer (i.e., 2 stacked Autoencoders).
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
conv_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28, 1], input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2)
])
conv_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="VALID", activation="selu",
input_shape=[3, 3, 64]),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="SAME", activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
conv_ae = keras.models.Sequential([conv_encoder, conv_decoder])
conv_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = conv_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=5,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
conv_encoder.summary()
conv_decoder.summary()
show_reconstructions(conv_ae)
plt.show()
Recurrent Autoencoders
recurrent_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.LSTM(100, return_sequences=True, input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.LSTM(30)
])
recurrent_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.RepeatVector(28, input_shape=[30]),
keras.layers.LSTM(100, return_sequences=True),
keras.layers.TimeDistributed(keras.layers.Dense(28, activation="sigmoid"))
])
recurrent_ae = keras.models.Sequential([recurrent_encoder, recurrent_decoder])
recurrent_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(0.1),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = recurrent_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10, validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(recurrent_ae)
plt.show()
Stacked denoising Autoencoder
Using Gaussian noise:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
denoising_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.GaussianNoise(0.2),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="selu")
])
denoising_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[30]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
denoising_ae = keras.models.Sequential([denoising_encoder, denoising_decoder])
denoising_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = denoising_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
noise = keras.layers.GaussianNoise(0.2)
show_reconstructions(denoising_ae, noise(X_valid, training=True))
plt.show()
Using dropout:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
dropout_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="selu")
])
dropout_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[30]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
dropout_ae = keras.models.Sequential([dropout_encoder, dropout_decoder])
dropout_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = dropout_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
dropout = keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)
show_reconstructions(dropout_ae, dropout(X_valid, training=True))
save_fig("dropout_denoising_plot", tight_layout=False)
Sparse Autoencoder
Let’s build a simple stacked autoencoder, so we can compare it to the sparse autoencoders we will build. This time we will use the sigmoid activation function for the coding layer, to ensure that the coding values range from 0 to 1:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
simple_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(30, activation="sigmoid"),
])
simple_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[30]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
simple_ae = keras.models.Sequential([simple_encoder, simple_decoder])
simple_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = simple_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(simple_ae)
plt.show()
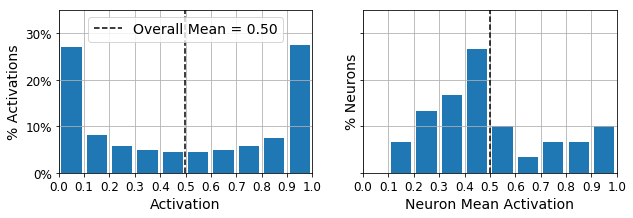
Let’s create a couple functions to print nice activation histograms:
def plot_percent_hist(ax, data, bins):
counts, _ = np.histogram(data, bins=bins)
widths = bins[1:] - bins[:-1]
x = bins[:-1] + widths / 2
ax.bar(x, counts / len(data), width=widths*0.8)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks(bins)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(mpl.ticker.FuncFormatter(
lambda y, position: "{}%".format(int(np.round(100 * y)))))
ax.grid(True)
def plot_activations_histogram(encoder, height=1, n_bins=10):
X_valid_codings = encoder(X_valid).numpy()
activation_means = X_valid_codings.mean(axis=0)
mean = activation_means.mean()
bins = np.linspace(0, 1, n_bins + 1)
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 3), nrows=1, ncols=2, sharey=True)
plot_percent_hist(ax1, X_valid_codings.ravel(), bins)
ax1.plot([mean, mean], [0, height], "k--", label="Overall Mean = {:.2f}".format(mean))
ax1.legend(loc="upper center", fontsize=14)
ax1.set_xlabel("Activation")
ax1.set_ylabel("% Activations")
ax1.axis([0, 1, 0, height])
plot_percent_hist(ax2, activation_means, bins)
ax2.plot([mean, mean], [0, height], "k--")
ax2.set_xlabel("Neuron Mean Activation")
ax2.set_ylabel("% Neurons")
ax2.axis([0, 1, 0, height])
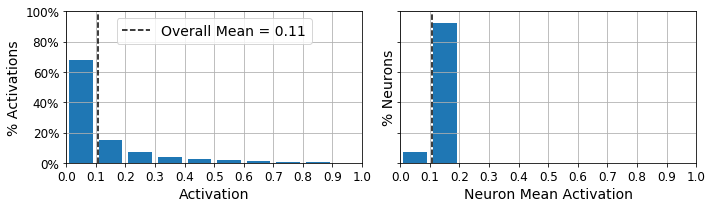
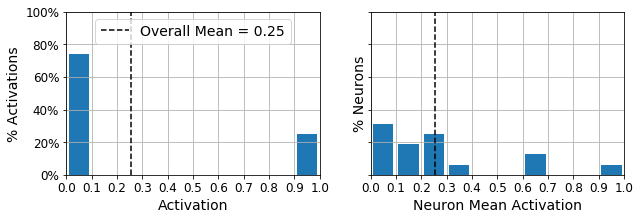
Let’s use these functions to plot histograms of the activations of the encoding layer. The histogram on the left shows the distribution of all the activations. You can see that values close to 0 or 1 are more frequent overall, which is consistent with the saturating nature of the sigmoid function. The histogram on the right shows the distribution of mean neuron activations: you can see that most neurons have a mean activation close to 0.5. Both histograms tell us that each neuron tends to either fire close to 0 or 1, with about 50% probability each. However, some neurons fire almost all the time (right side of the right histogram).
plot_activations_histogram(simple_encoder, height=0.35)
plt.show()
Now let’s add $\ell_1$ regularization to the coding layer:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
sparse_l1_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(300, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.ActivityRegularization(l1=1e-3) # Alternatively, you could add
# activity_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l1(1e-3)
# to the previous layer.
])
sparse_l1_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[300]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
sparse_l1_ae = keras.models.Sequential([sparse_l1_encoder, sparse_l1_decoder])
sparse_l1_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = sparse_l1_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(sparse_l1_ae)
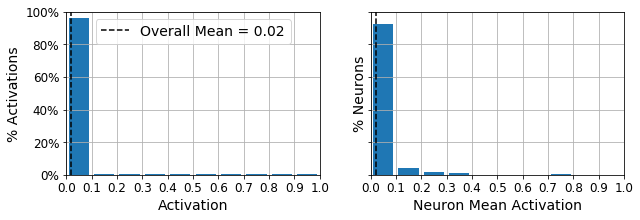
plot_activations_histogram(sparse_l1_encoder, height=1.)
plt.show()
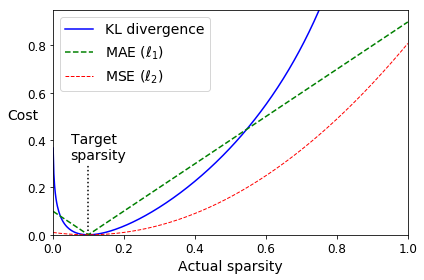
Let’s use the KL Divergence loss instead to ensure sparsity, and target 10% sparsity rather than 0%:
p = 0.1
q = np.linspace(0.001, 0.999, 500)
kl_div = p * np.log(p / q) + (1 - p) * np.log((1 - p) / (1 - q))
mse = (p - q)**2
mae = np.abs(p - q)
plt.plot([p, p], [0, 0.3], "k:")
plt.text(0.05, 0.32, "Target\nsparsity", fontsize=14)
plt.plot(q, kl_div, "b-", label="KL divergence")
plt.plot(q, mae, "g--", label=r"MAE ($\ell_1$)")
plt.plot(q, mse, "r--", linewidth=1, label=r"MSE ($\ell_2$)")
plt.legend(loc="upper left", fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel("Actual sparsity")
plt.ylabel("Cost", rotation=0)
plt.axis([0, 1, 0, 0.95])
save_fig("sparsity_loss_plot")
K = keras.backend
kl_divergence = keras.losses.kullback_leibler_divergence
class KLDivergenceRegularizer(keras.regularizers.Regularizer):
def __init__(self, weight, target=0.1):
self.weight = weight
self.target = target
def __call__(self, inputs):
mean_activities = K.mean(inputs, axis=0)
return self.weight * (
kl_divergence(self.target, mean_activities) +
kl_divergence(1. - self.target, 1. - mean_activities))
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
kld_reg = KLDivergenceRegularizer(weight=0.05, target=0.1)
sparse_kl_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(300, activation="sigmoid", activity_regularizer=kld_reg)
])
sparse_kl_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[300]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
sparse_kl_ae = keras.models.Sequential([sparse_kl_encoder, sparse_kl_decoder])
sparse_kl_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = sparse_kl_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(sparse_kl_ae)
plot_activations_histogram(sparse_kl_encoder)
save_fig("sparse_autoencoder_plot")
plt.show()
Variational Autoencoder
class Sampling(keras.layers.Layer):
def call(self, inputs):
mean, log_var = inputs
return K.random_normal(tf.shape(log_var)) * K.exp(log_var / 2) + mean
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
codings_size = 10
inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=[28, 28])
z = keras.layers.Flatten()(inputs)
z = keras.layers.Dense(150, activation="selu")(z)
z = keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu")(z)
codings_mean = keras.layers.Dense(codings_size)(z)
codings_log_var = keras.layers.Dense(codings_size)(z)
codings = Sampling()([codings_mean, codings_log_var])
variational_encoder = keras.models.Model(
inputs=[inputs], outputs=[codings_mean, codings_log_var, codings])
decoder_inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=[codings_size])
x = keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu")(decoder_inputs)
x = keras.layers.Dense(150, activation="selu")(x)
x = keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid")(x)
outputs = keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])(x)
variational_decoder = keras.models.Model(inputs=[decoder_inputs], outputs=[outputs])
_, _, codings = variational_encoder(inputs)
reconstructions = variational_decoder(codings)
variational_ae = keras.models.Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=[reconstructions])
latent_loss = -0.5 * K.sum(
1 + codings_log_var - K.exp(codings_log_var) - K.square(codings_mean),
axis=-1)
variational_ae.add_loss(K.mean(latent_loss) / 784.)
variational_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="rmsprop", metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = variational_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=25, batch_size=128,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(variational_ae)
plt.show()
Generate Fashion Images
def plot_multiple_images(images, n_cols=None):
n_cols = n_cols or len(images)
n_rows = (len(images) - 1) // n_cols + 1
if images.shape[-1] == 1:
images = np.squeeze(images, axis=-1)
plt.figure(figsize=(n_cols, n_rows))
for index, image in enumerate(images):
plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, index + 1)
plt.imshow(image, cmap="binary")
plt.axis("off")
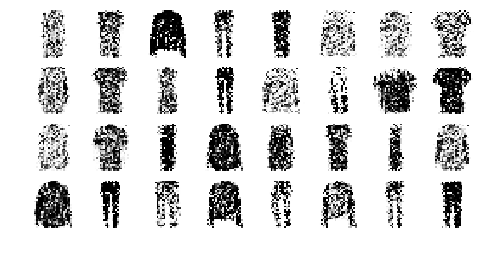
Let’s generate a few random codings, decode them and plot the resulting images:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
codings = tf.random.normal(shape=[12, codings_size])
images = variational_decoder(codings).numpy()
plot_multiple_images(images, 4)
save_fig("vae_generated_images_plot", tight_layout=False)
Now let’s perform semantic interpolation between these images:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
codings_grid = tf.reshape(codings, [1, 3, 4, codings_size])
larger_grid = tf.image.resize(codings_grid, size=[5, 7])
interpolated_codings = tf.reshape(larger_grid, [-1, codings_size])
images = variational_decoder(interpolated_codings).numpy()
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
for index, image in enumerate(images):
plt.subplot(5, 7, index + 1)
if index%7%2==0 and index//7%2==0:
plt.gca().get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.gca().get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
else:
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(image, cmap="binary")
save_fig("semantic_interpolation_plot", tight_layout=False)
Generative Adversarial Networks
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
codings_size = 30
generator = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[codings_size]),
keras.layers.Dense(150, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
discriminator = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(150, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")
])
gan = keras.models.Sequential([generator, discriminator])
discriminator.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="rmsprop")
discriminator.trainable = False
gan.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="rmsprop")
batch_size = 32
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(X_train).shuffle(1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True).prefetch(1)
def train_gan(gan, dataset, batch_size, codings_size, n_epochs=50):
generator, discriminator = gan.layers
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
print("Epoch {}/{}".format(epoch + 1, n_epochs)) # not shown in the book
for X_batch in dataset:
# phase 1 - training the discriminator
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[batch_size, codings_size])
generated_images = generator(noise)
X_fake_and_real = tf.concat([generated_images, X_batch], axis=0)
y1 = tf.constant([[0.]] * batch_size + [[1.]] * batch_size)
discriminator.trainable = True
discriminator.train_on_batch(X_fake_and_real, y1)
# phase 2 - training the generator
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[batch_size, codings_size])
y2 = tf.constant([[1.]] * batch_size)
discriminator.trainable = False
gan.train_on_batch(noise, y2)
plot_multiple_images(generated_images, 8) # not shown
plt.show() # not shown
train_gan(gan, dataset, batch_size, codings_size, n_epochs=1)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[batch_size, codings_size])
generated_images = generator(noise)
plot_multiple_images(generated_images, 8)
save_fig("gan_generated_images_plot", tight_layout=False)
train_gan(gan, dataset, batch_size, codings_size)
Deep Convolutional GAN
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
codings_size = 100
generator = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(7 * 7 * 128, input_shape=[codings_size]),
keras.layers.Reshape([7, 7, 128]),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="SAME",
activation="selu"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="SAME",
activation="tanh"),
])
discriminator = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="SAME",
activation=keras.layers.LeakyReLU(0.2),
input_shape=[28, 28, 1]),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.4),
keras.layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=5, strides=2, padding="SAME",
activation=keras.layers.LeakyReLU(0.2)),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.4),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")
])
gan = keras.models.Sequential([generator, discriminator])
discriminator.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="rmsprop")
discriminator.trainable = False
gan.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer="rmsprop")
X_train_dcgan = X_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1) * 2. - 1. # reshape and rescale
batch_size = 32
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(X_train_dcgan)
dataset = dataset.shuffle(1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True).prefetch(1)
train_gan(gan, dataset, batch_size, codings_size)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
noise = tf.random.normal(shape=[batch_size, codings_size])
generated_images = generator(noise)
plot_multiple_images(generated_images, 8)
save_fig("dcgan_generated_images_plot", tight_layout=False)
Exercise Solutions
Unsupervised pretraining
Let’s create a small neural network for MNIST classification:
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
X_train_small = X_train[:500]
y_train_small = y_train[:500]
classifier = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28, 1], input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="SAME", activation="selu"),
keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(20, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax")
])
classifier.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.02),
metrics=["accuracy"])
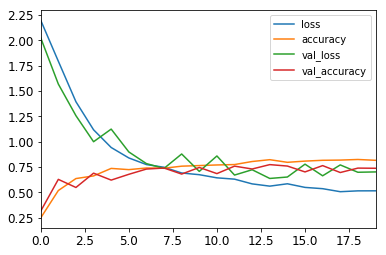
history = classifier.fit(X_train_small, y_train_small, epochs=20, validation_data=[X_valid, y_valid])
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(history.history).plot()
plt.show()
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
conv_encoder_clone = keras.models.clone_model(conv_encoder)
pretrained_clf = keras.models.Sequential([
conv_encoder_clone,
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(20, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax")
])
conv_encoder_clone.trainable = False
pretrained_clf.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy",
optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.02),
metrics=["accuracy"])
history = pretrained_clf.fit(X_train_small, y_train_small, epochs=30,
validation_data=[X_valid, y_valid])
conv_encoder_clone.trainable = True
pretrained_clf.compile(loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy",
optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.02),
metrics=["accuracy"])
history = pretrained_clf.fit(X_train_small, y_train_small, epochs=20,
validation_data=[X_valid, y_valid])
Hashing Using a Binary Autoencoder
tf.random.set_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
hashing_encoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[28, 28]),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu"),
keras.layers.GaussianNoise(15.),
keras.layers.Dense(16, activation="sigmoid"),
])
hashing_decoder = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="selu", input_shape=[16]),
keras.layers.Dense(28 * 28, activation="sigmoid"),
keras.layers.Reshape([28, 28])
])
hashing_ae = keras.models.Sequential([hashing_encoder, hashing_decoder])
hashing_ae.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1.0),
metrics=[rounded_accuracy])
history = hashing_ae.fit(X_train, X_train, epochs=10,
validation_data=[X_valid, X_valid])
show_reconstructions(hashing_ae)
plt.show()
plot_activations_histogram(hashing_encoder)
plt.show()
hashes = np.round(hashing_encoder.predict(X_valid)).astype(np.int32)
hashes *= np.array([[2**bit for bit in range(16)]])
hashes = hashes.sum(axis=1)
for h in hashes[:5]:
print("{:016b}".format(h))
print("...")
n_bits = 4
n_images = 8
plt.figure(figsize=(n_images, n_bits))
for bit_index in range(n_bits):
in_bucket = (hashes & 2**bit_index != 0)
for index, image in zip(range(n_images), X_valid[in_bucket]):
plt.subplot(n_bits, n_images, bit_index * n_images + index + 1)
plt.imshow(image, cmap="binary")
plt.axis("off")